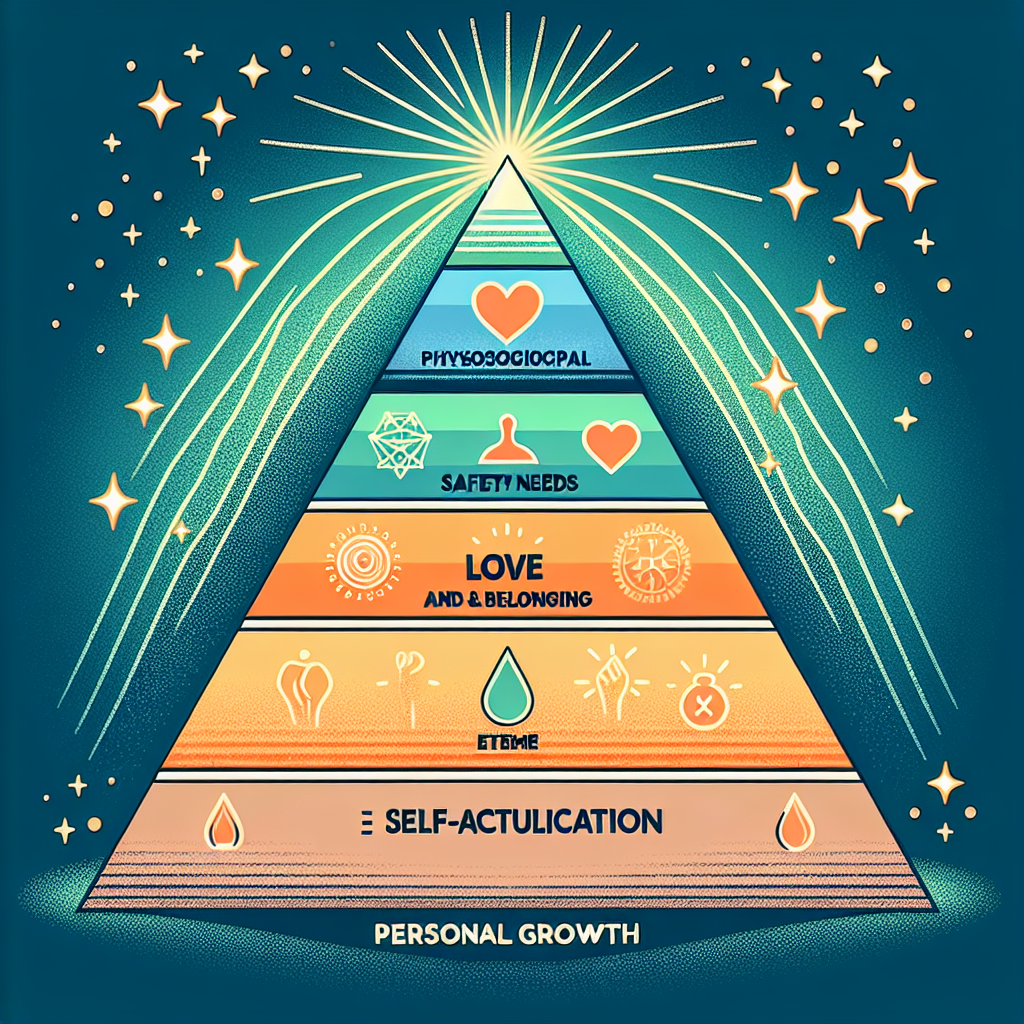
Maslow’s Blueprint for Growth: Understanding Each Level of the Hierarchy
Introduction
In a world constantly in flux, understanding how to achieve personal and professional growth is essential. Enter Maslow’s Blueprint for Growth: Understanding Each Level of the Hierarchy, a transformative framework that not only sheds light on human motivation but also serves as a roadmap for meaningful development. At the crux of Maslow’s theory lies an intuitive insight: to reach our fullest potential, we must understand and navigate the varied layers of our needs. This article will delve into this hierarchy, exploring each level, case studies, and actionable insights, ultimately inspiring you to embark on your unique growth journey.
The Foundation: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
What Is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
At its core, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological framework introduced by Abraham Maslow in 1943. The theory proposes that human needs can be organized into five distinct levels, arranged in a pyramid structure, often depicted visually to illustrate how lower-level needs must be met before progressing to higher-level psychological and self-fulfillment needs.
The Five Levels Explained
-
Physiological Needs: These are the most basic human needs for survival, including food, water, shelter, and sleep.
-
Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are satisfied, individuals seek safety and security—both physically and emotionally.
-
Love and Belongingness Needs: This level focuses on social relationships, the need for affection, and a sense of connection.
-
Esteem Needs: Here, we find the desire for self-esteem, respect, and recognition from others.
- Self-Actualization Needs: The pinnacle of the hierarchy involves realizing personal potential, self-fulfillment, and pursuing creative activities.
Visual Representation
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Physiological Needs | Basic survival requirements |
| Safety Needs | Security and stability |
| Love and Belongingness | Relationships and social connections |
| Esteem Needs | Self-esteem and recognition |
| Self-Actualization Needs | Personal growth and fulfillment |
Diving Deeper: Understanding Each Level
1. Physiological Needs: The Ground Level
Physiological needs form the base of Maslow’s pyramid, serving as the critical foundation for all subsequent growth. This category encompasses basic survival requirements—food, water, shelter, and sleep. For individuals, these needs often dictate their ability to focus on higher-order needs.
Case Study: Homelessness and Mental Health
In a seminal study conducted in the United States, researchers found that individuals experiencing homelessness struggled primarily with meeting these basic physiological needs. As a result, they could not focus on social connections or self-esteem, demonstrating how foundational needs impact overall mental health.
2. Safety Needs: Building a Secure Base
Once physiological needs are met, individuals instinctively seek safety and security. This includes personal safety, financial security, and health. A sense of security is vital to thrive and pursue higher aspirations.
Case Study: Corporate Security Policies
Companies like Google have implemented comprehensive security measures, satisfying employees’ safety needs and fostering a more innovative environment. By addressing these needs, they cultivate a workplace where creativity flourishes.
3. Love and Belongingness Needs: The Social Bond
As human beings, we thrive on relationships and social connections. Once safety needs are established, we seek love, friendship, and a sense of belonging. This level emphasizes the importance of interpersonal relationships.
Case Study: The Impact of Social Media
Research indicates that social media platforms, while often criticized, have bridged gaps for isolated individuals. By fostering connections, these platforms have helped fulfill love and belonging needs, proving their relevance in today’s society.
4. Esteem Needs: Seeking Recognition
The fourth level encompasses both self-esteem and esteem from others. Recognition, respect, and a sense of accomplishment are vital ingredients for personal growth.
Case Study: Employee Recognition Programs
Organizations implementing employee recognition programs—such as Google’s peer-to-peer acknowledgment system—demonstrate the significance of esteeming needs. Employees report higher satisfaction and productivity levels, confirming that recognition is a powerful motivator.
5. Self-Actualization Needs: Reaching Potential
At the top of the hierarchy lies self-actualization—the desire to become the most that one can be. This level emphasizes personal growth, creativity, and fulfillment.
Case Study: Artists and Innovators
Famous figures like Vincent van Gogh exemplify self-actualization. Despite facing numerous challenges, they pursued their passions and ultimately achieved significant creative contributions, underscoring the importance of fostering an environment where self-actualization can thrive.
Navigating Maslow’s Blueprint for Growth
The Importance of Progression
Understanding Maslow’s Blueprint for Growth: Understanding Each Level of the Hierarchy involves recognizing that growth is a journey. It’s essential to first meet the needs at one level before advancing to the next.
Self-Assessment: Where Are You?
To effectively climb Maslow’s pyramid, perform a self-assessment. Ask yourself:
- Are my basic needs met?
- Do I feel safe and secure?
- Do I have meaningful relationships?
- Am I recognized for my accomplishments?
Strategies for Advancing Through the Levels
1. Focus on Basic Needs
If you’re struggling with physiological needs, consider developing a budget to ensure food security or applying for assistance programs.
2. Promote a Safe Environment
At work or home, establish boundaries that enhance your sense of safety. This could involve open communication about concerns or creating a supportive community.
3. Cultivate Relationships
Invest time in connections with family and friends. Engage in community activities that foster a sense of belonging.
4. Seek Recognition
Don’t shy away from sharing your accomplishments. Engage with mentors who can provide constructive feedback and acknowledgment.
5. Pursue Self-Actualization
Explore new hobbies, volunteer, or take up creative projects. Engage in activities that resonate with your core identities and aspirations.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Maslow’s Blueprint for Growth: Understanding Each Level of the Hierarchy provides invaluable insights into personal development. By comprehensively understanding each level and striving to meet those needs, we can progress toward a fulfilling, self-actualized life. Remember, growth is a journey shaped by experiences, relationships, and a commitment to self-discovery.
Actionable Insights
- Assess your current needs and create a plan to address them.
- Surround yourself with supportive individuals who encourage growth.
- Take small but consistent steps toward your self-actualization goals.
FAQs
1. What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological framework that categorizes human needs into five levels, from physiological to self-actualization.
2. How can I apply Maslow’s theory to my life?
Begin by assessing which level of needs you need to satisfy first and create a plan to address them progressively.
3. What happens if lower needs are not met?
If lower-level needs are unmet, it can hinder your ability to focus on higher-level needs, leading to stagnation in personal growth.
4. Can you skip levels in Maslow’s hierarchy?
The theory suggests that levels are sequential and should typically be addressed in order; however, individual experiences may vary.
5. How does self-actualization affect my overall well-being?
Self-actualization leads to greater fulfillment, purpose, and overall life satisfaction, positively impacting your mental and emotional health.
By engaging with Maslow’s framework, you can cultivate a deeper understanding of yourself and your growth journey, ensuring each step is meaningful and fulfilling.