Stages of Understanding: How Cognitive Development Shapes Our World
Introduction
In our rapidly changing world, the intricate dance of human cognition serves as the foundation for learning, decision-making, and interaction. Understanding the stages of understanding—the development of our cognitive abilities—provides profound insights into how we perceive reality, navigate challenges, and thrive in various environments. If you’ve ever wondered why children learn differently than adults, or how cognitive development impacts education, parenting, and even policy-making, you’ve come to the right place.
This article delves into stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world. We’ll explore the theories of leading psychologists, uncover startling case studies, and provide actionable insights on how these principles apply in our daily lives. Join us on this eye-opening journey as we unravel the layers of cognitive development and its far-reaching implications.
Theoretical Foundations of Cognitive Development
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
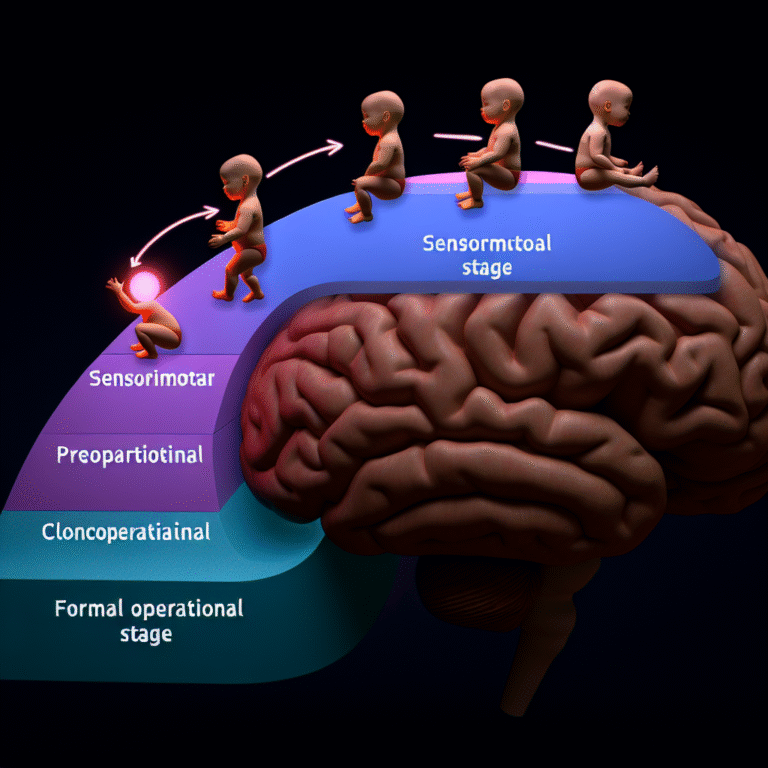
One of the cornerstone theories in cognitive development is Jean Piaget’s framework, which outlines four primary stages that children experience as they grow. These stages are:
- Sensorimotor Stage (0-2 years): Knowledge is acquired through sensory experiences and manipulating objects.
- Preoperational Stage (2-7 years): Children begin to think symbolically but lack the ability to perform operations mentally.
- Concrete Operational Stage (7-11 years): Logical thinking develops, but it is typically limited to concrete objects and events.
- Formal Operational Stage (12 years and older): Abstract reasoning and logical thought processes emerge.
Piaget’s theory provides a roadmap for understanding how children interpret their surroundings, emphasizing the importance of active engagement with their environment in shaping cognitive abilities. This progression underscores the essence of stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world.
Case Study: Piaget in Action
A study conducted in a local preschool illustrated Piaget’s theories in practice. Researchers observed children engaged in play with blocks, where the older children (in the Concrete Operational Stage) successfully constructed elaborate structures, demonstrating spatial awareness and logical reasoning. In contrast, younger children (in the Preoperational Stage) focused more on imaginative play without the same structural understanding.
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory
Vygotsky argued that social interactions and cultural context significantly influence cognitive development. His concept of the "Zone of Proximal Development" (ZPD) emphasizes the importance of guidance and collaboration in learning. According to Vygotsky, children learn best when they engage with more knowledgeable peers or adults who can introduce new concepts.
Table: Comparison of Piaget and Vygotsky
| Feature | Piaget’s Theory | Vygotsky’s Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Stages of development | Social context and interactions |
| Key Processes | Individual exploration | Cooperative dialogue |
| Role of Language | Secondary to cognitive growth | Integral to cognitive growth |
| Learning Environment | Evolving through personal experimentation | Collaboratively constructed learning |
Understanding these theories sheds light on stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world from different angles. Both frameworks contribute significantly to educational practices today.
Real-World Applications of Cognitive Development Insights
Educational Strategies
In schools, recognizing the stages of cognitive development allows educators to tailor their teaching methods effectively. For example, primary school teachers often use hands-on activities to engage children in the Concrete Operational Stage. This playful learning helps solidify concepts in a way that resonates with their cognitive abilities.
During a recent workshop, educators learned how embedding Vygotsky’s ideas into their curriculum—for instance, through group projects—enhanced collaboration among students, allowing them to explore topics more deeply and understand complex ideas through shared experiences.
Parenting Styles and Cognitive Growth
Parents can apply knowledge of cognitive development stages to support their children’s growth. For instance, parents with toddlers often engage them in playful interactions that stimulate sensory and motor skills. As children grow, encouraging problem-solving through games can enhance critical thinking during the Concrete Operational Stage.
Case Study: Parenting and Cognitive Development
A longitudinal study tracked children from birth to adulthood, focusing on their cognitive development while observing parenting styles. The results indicated that children whose parents practiced supportive yet challenging learning environments—providing appropriate challenges just beyond their current capabilities—tended to excel academically and socially. This aligns with Vygotsky’s ZPD, reinforcing the importance of the right support during various stages of understanding.
Workplace Learning and Development
Understanding cognitive development can revolutionize training programs in organizations. By acknowledging the differing cognitive levels of adult learners, corporate trainers can design curricula that resonate with employees’ experiences and developmental stages. For instance, the introduction of mentorship programs allows for the transfer of knowledge and skills from seasoned employees to newcomers, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Table: Implications for Educational and Workplace Training Programs
| Stage of Development | Educational Approach | Workplace Training Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Sensorimotor | Exploratory, sensory-rich activities | Hands-on demonstrations |
| Preoperational | Symbolic play and storytelling | Creative team-building exercises |
| Concrete Operational | Concrete examples, problem-solving | Structured workshops |
| Formal Operational | Abstract concepts, critical discussion | Strategic planning sessions |
Incorporating cognitive development strategies in both educational and workplace settings exemplifies how the stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world translate into practical initiatives that foster growth.
The Technology Factor: Cognitive Development in a Digital Age
In today’s digital landscape, technology plays a pivotal role in shaping cognitive development. Apps and online learning platforms offer expansive resources that cater to various stages of understanding. Educators and parents can incorporate these tools to enhance learning experiences.
Case Study: Digital Learning Impact
A recent study examined a cohort of students learning mathematics through a popular educational app. Despite initial concerns regarding screen time, the findings showed that students using gamified learning methods exhibited improved problem-solving skills and increased engagement compared to traditional classroom settings. This illustrates how technology can effectively supplement cognitive growth, adapting to the needs of various stages of understanding.
Considering Risks
While technology can accelerate learning and engagement, it’s crucial to balance screen time with hands-on activities. Over-reliance on digital devices could hinder the natural exploration and social interaction vital for cognitive development.
Conclusion
Understanding the stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world is fundamental not only for educators and parents but for everyone who interacts within the communities we inhabit. This knowledge allows us to create environments that nurture growth, whether through tailored educational methodologies, mindful parenting approaches, or innovative workplace initiatives. By fostering an awareness of cognitive development, we equip ourselves to build a more supportive world—one that appreciates the varied capabilities of learners of all ages.
As you reflect on the insights shared throughout this article, consider how you can apply these principles in your own life, whether in your teaching, parenting, or professional endeavors. The journey of understanding is ongoing, and every step makes a difference.
FAQs
1. What are the main stages of cognitive development according to Piaget?
Piaget identified four stages: Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational.
2. How does Vygotsky’s theory differ from Piaget’s?
While Piaget focused on individual exploration, Vygotsky emphasized the role of social interactions and cultural context in cognitive development.
3. Can technology negatively impact cognitive development?
Yes, over-reliance on technology can hinder natural exploration and social interaction, vital for cognitive growth.
4. How can parents support their child’s cognitive development?
Parents can engage children in age-appropriate activities, promote problem-solving skills, and provide supportive learning environments.
5. Are there practical applications of cognitive development theories in the workplace?
Absolutely! Understanding cognitive development can guide training programs, mentorship initiatives, and collaborative projects that enhance learning and productivity.
By embedding the Insights gained from the stages of understanding: how cognitive development shapes our world, we create a more nurturing environment that caters to individuals of all ages and learning stages. Whether you’re an educator, a parent, or a professional, the principles discussed here can make a lasting impact. Embrace the journey of understanding—our world is shaped by the ways we learn together.