Introduction
Imagine walking through a bustling city, vibrant colors splashing across billboards, shadows dancing on sidewalks, and the rhythmic movement of people all around you. Our ability to decode this chaos stems from a marvelously intricate process known as visual perception. Understanding visual perception: how our eyes and brain collaborate unveils the incredible mechanisms that allow us to interpret the world around us. This collaboration is not just a biological function; it’s a profound interplay that impacts everything from our daily interactions to our artistic expressions.
The Basics of Visual Perception
What is Visual Perception?
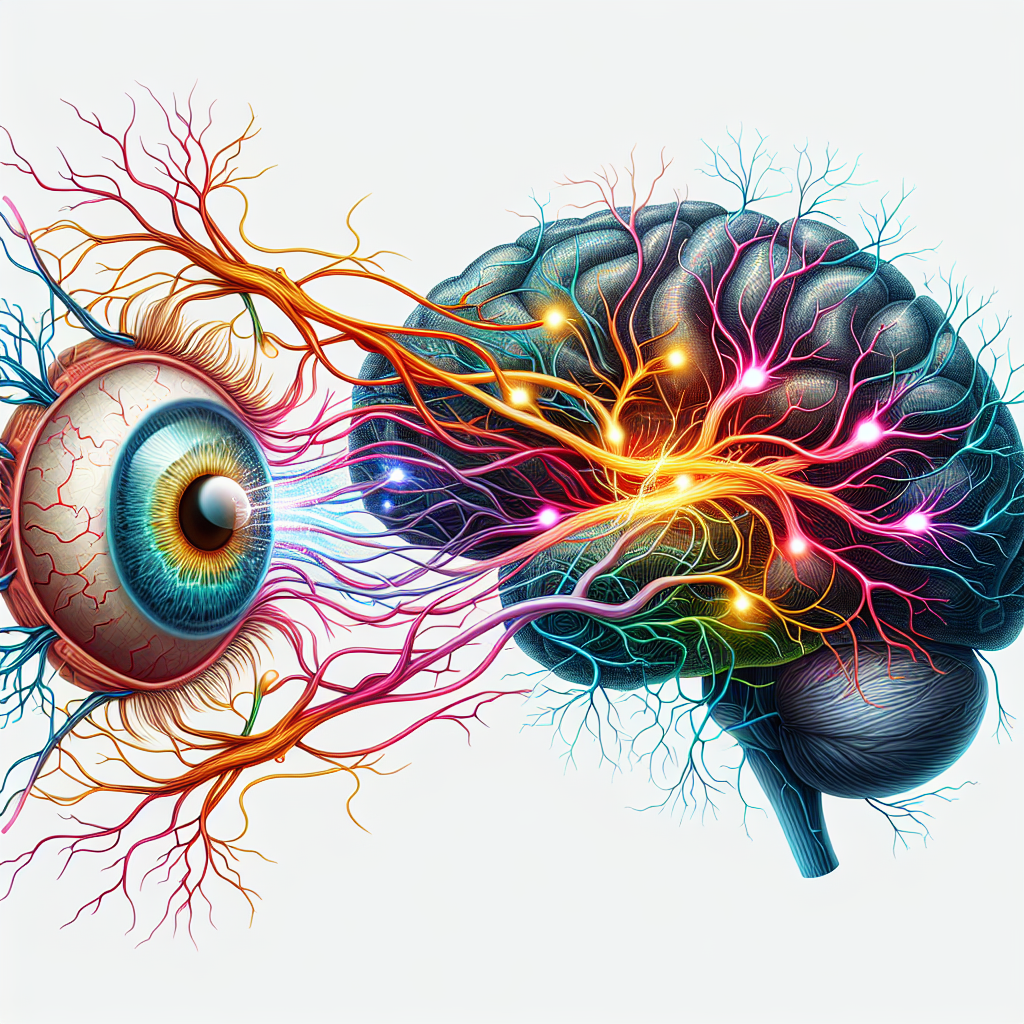
Visual perception refers to the process through which our brains interpret and make sense of the visual information our eyes receive. This complex mechanism involves several steps: light enters the eye, is transformed into neural signals, and is then interpreted by the brain. The result? Our ability to interact meaningfully with our environment.
Key Components of Visual Perception
- The Eye: The gateway to visual information, comprising structures like the cornea, lens, and retina.
- Neural Pathways: These are the conduits through which visual information travels from the eye to the brain.
- The Brain: Specifically, the occipital lobe, where visual information is processed and interpreted.
The Science Behind Visual Perception
The Journey of Light
When light strikes an object, it bounces off and enters our eyes, specifically through the cornea, then passes through the lens, which focuses it onto the retina at the back of the eye. Photoreceptors (rods and cones) in the retina transform this light into electrical signals.
Neural Processing
Once the retina converts light into signals, these signals are relayed through the optic nerve to the brain’s visual cortex. The brain decodes these signals, allowing us to recognize shapes, colors, and movements, culminating in what we perceive as "sight."
Processing Visual Information
- Top-Down Processing: Our brain uses prior knowledge and expectations to interpret visual stimuli.
- Bottom-Up Processing: Here, our perception begins with basic sensory information and builds up to complex perceptions.
Case Study: The Stroop Effect
The Stroop Effect illustrates the interaction between reading and color perception. In one experiment, participants were shown words that named colors (like "red," "blue") but were printed in conflicting ink colors (e.g., the word "red" in blue ink). Most participants found it harder to name the ink color, showcasing how our cognitive processes can sometimes conflict—demonstrating the nuance in understanding visual perception: how our eyes and brain collaborate.
Analysis of the Stroop Effect
The Stroop Effect emphasizes how automatic cognitive processes (reading) can interfere with conscious efforts (naming colors). This phenomenon has implications for understanding attention and processing in various real-world scenarios, including everything from education to design.
Implications of Visual Perception
Art and Design
Understanding visual perception: how our eyes and brain collaborate heavily influences fields like art and design. Artists often use color theory and composition strategies to guide how viewers engage with their work.
Marketing Strategies
In advertising, companies capitalize on visual perception principles to create compelling messages that capture attention and provoke desire. Brands craft striking visuals to ensure they resonate with consumers, proving how intertwined our visual capabilities are with decision-making.
Visual Perception in Technology
Augmented and Virtual Reality
Understanding visual perception informs the development of augmented and virtual realities (VR). These technologies simulate real-world environments, capitalizing on how our eyes and brains process depth, motion, and spatial awareness.
Adaptive Interfaces
Tech firms are increasingly designing adaptive interfaces that cater to human visual perception capabilities. For instance, changing color contrasts can enhance usability for users with visual impairments.
Challenges and Advances in Visual Perception Research
Conditions Affecting Visual Perception
Disorders like prosopagnosia (difficulty recognizing faces) and agnosia (inability to interpret sensations) highlight how intricate and crucial visual perception is. Understanding these conditions allows scientists and medical professionals to enhance diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions.
Emerging Research
Recent studies explore neural plasticity—how our brain adapts with experience. For instance, research on how blind individuals utilize other senses to compensate for the lack of visual input deepens our understanding of human cognition and adaptability.
Enhancing Your Understanding of Visual Perception
Practical Exercises
- Mindful Observation: Spend time observing your surroundings, noting colors, shapes, and movement. This enhances awareness and makes you more attuned to how your brain organizes visual information.
- Artistic Play: Engage in drawing or painting. This helps reinforce how our visual perception can be transformed into creative expression.
Resources for Further Learning
- Books: "Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology" explores the complexities of visual perception.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera offer courses on neuroscience and psychology related to perception.
Conclusion
Understanding visual perception: how our eyes and brain collaborate is essential not just for personal knowledge but for its applications across various fields. From art to technology, recognizing how these components interact enriches our appreciation of the world. As we continue to explore visual perception, we gain insights that can help us design better experiences, learn more effectively, and even appreciate the depth of artistic creations.
FAQs
-
What is the role of the retina in visual perception?
- The retina contains photoreceptors that convert light into signals essential for visual processing.
-
How do our brains interpret colors?
- The brain interprets colors based on the wavelengths of light that are absorbed or reflected by objects.
-
What conditions can affect visual perception?
- Conditions like color blindness, prosopagnosia, and agnosia can severely alter one’s ability to perceive visual information.
-
Can visual perception be improved?
- Yes, engaging in activities like mindful observation and practice in art can enhance visual skills.
- How does visual perception relate to technology like VR?
- Understanding visual perception is crucial for creating realistic environments in virtual and augmented reality, ensuring user engagement and immersion.
In this enlightening exploration of visual perception, we’ve distilled complex processes and real-world implications into practical insights. Remember, every time you open your eyes, a spectacular collaboration between your eyes and brain brings the world to life. Embrace that marvel!