Introduction
Have you ever wondered why some people can eat whatever they want and remain slim while others struggle to lose weight no matter how hard they try? This enduring mystery often revolves around one crucial element: hormones. The power of hormones goes beyond just the physical; they can dictate our cravings, our energy levels, and even how we burn calories. Understanding how they influence weight, appetite, and metabolism can empower us to make more informed choices about our health and well-being. Let’s unravel the complex interplay of hormones and discover actionable insights that could transform your life.
The Science Behind Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by glands in our endocrine system. They travel through the bloodstream to various tissues and organs, orchestrating critical physiological functions. The power of hormones stems from their ability to regulate everything from mood to metabolism. To truly appreciate how they influence weight and appetite, it’s essential to understand their roles.
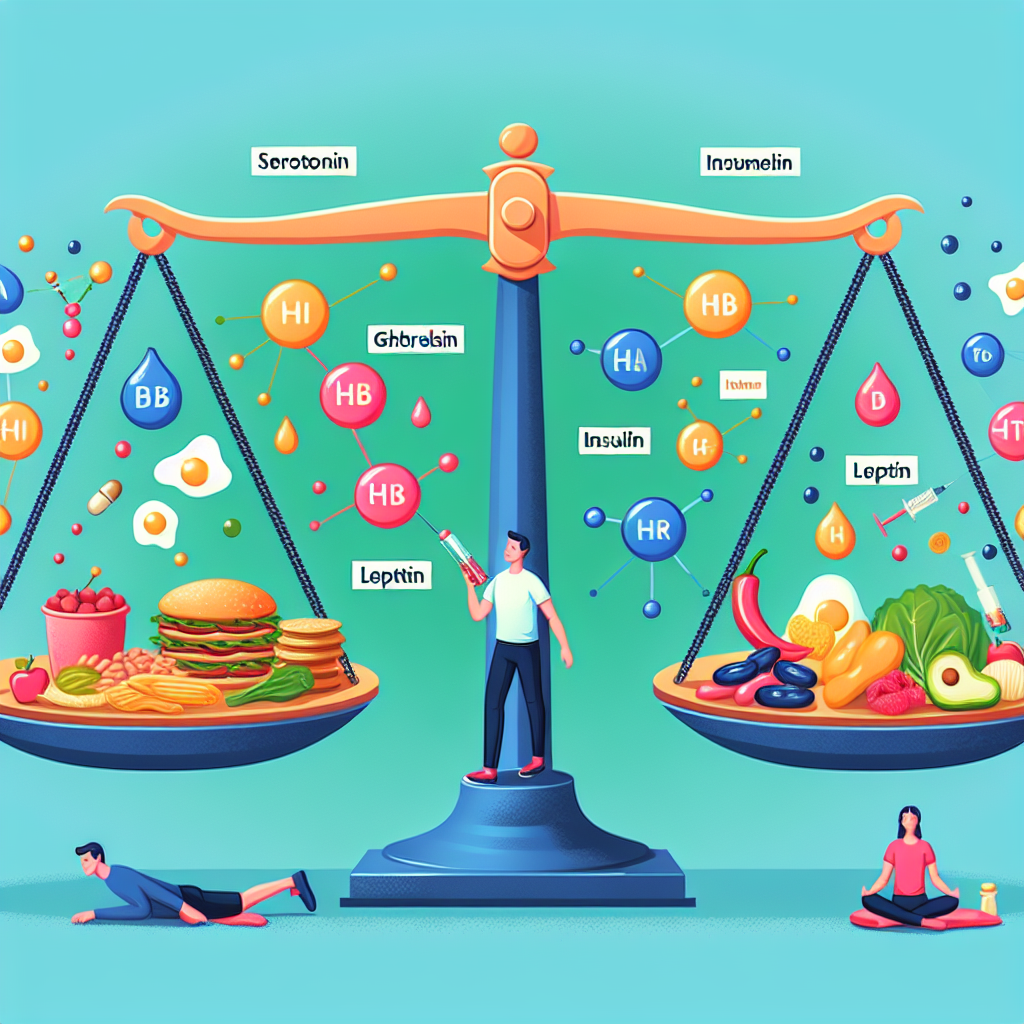
Key Hormones Involved in Weight Control
Leptin: Often regarded as the "satiety hormone," leptin is produced by fat cells and signals the brain when to stop eating. Higher levels of leptin are typically observed in obese individuals, but their brains can become resistant to this hormone, leading to continuous eating.
Ghrelin: Known as the "hunger hormone," ghrelin is secreted by the stomach and stimulates appetite. Levels tend to rise before meals and fall after eating. Elevated ghrelin levels can drive hunger, making it challenging to stick to a diet.
Insulin: Produced by the pancreas, insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels. It also plays a significant role in fat storage. Chronic high insulin levels can lead to weight gain and may promote the development of insulin resistance.
- Cortisol: Often referred to as the "stress hormone," cortisol can lead to increased appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods when elevated over long periods.
How Hormones Affect Appetite
Hormones dictate when and how much we eat. Understanding these signals is crucial for managing our weight effectively.
The Lep-grelin Balancing Act
Research shows that balancing leptin and ghrelin can help control appetite effectively. In a notable study published in Obesity, researchers found that participants with lower leptin levels were more likely to overeat. By tracking their hormone levels over time, it was discovered that successful dieters tended to have a more balanced ratio of leptin to ghrelin, leading to better control over their appetite.
| Hormone | Function | Effects on Appetite |
|---|---|---|
| Leptin | Signals fullness | Reduces hunger |
| Ghrelin | Signals hunger | Increases appetite |
Stress and Eating: The Cortisol Connection
Cortisol can significantly impact our eating behaviors. Elevated levels due to stress can trigger cravings for sugary, high-fat foods. A case study involving college students during exam season found that those with higher cortisol levels tended to consume more snacks and gain weight.
The Metabolism Connection
Hormones are not just about appetite; they play a pivotal role in metabolism as well. Metabolism refers to the biochemical processes that convert food into energy.
Thyroid Hormones: The Metabolic Engine
Thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are crucial for regulating metabolic rate. Low levels of these hormones can lead to weight gain due to a slower metabolism. A clinical trial involving hypothyroid patients showed that hormone replacement therapy led to significant weight loss and improved metabolic functions.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case Study 1: The Leptin-Resistant Obese Individual
In a patient diagnosed with leptin resistance, a structured dietary change focusing on reducing refined carbs and sugars helped modulate hormone levels. After a few months, the individual experienced a significant decrease in hunger and regained control over their appetite. This case highlights the critical role of hormonal balance in weight management.
Case Study 2: Stress Management and Weight Loss
In a therapeutic study focusing on stress management techniques, participants who engaged in mindfulness and relaxation experienced lower cortisol levels and subsequently reported reduced cravings and weight loss. This underscores the impact of emotional well-being on hormonal regulation.
Tips for Harnessing the Power of Hormones
Understanding how to utilize the power of hormones effectively can help you manage your weight, appetite, and metabolism better. Here are some actionable insights:
Focus on Whole Foods: High-fiber foods help enhance leptin sensitivity, while balanced meals can regulate ghrelin levels. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises that can help lower cortisol levels.
Sleep Matters: Lack of sleep can elevate ghrelin and lower leptin, leading to increased hunger. Aim for at least 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate hormone levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger. Drinking plenty of water can help you regulate appetite naturally.
Conclusion
The power of hormones is profound and multifaceted, influencing not only our weight but also our appetite and metabolism. By understanding which hormones are at play and how they operate, we can take actionable steps towards better health outcomes. Whether it’s managing stress, improving sleep quality, or making smarter dietary choices, the insights gained from hormonal awareness empower us with the knowledge needed to make lasting changes.
FAQs
1. How do hormones affect weight gain?
Hormones like insulin, cortisol, and ghrelin can promote weight gain by increasing appetite or altering fat storage.
2. Can lifestyle changes influence hormone levels?
Yes, diet, exercise, and stress management can positively affect hormone levels, leading to better appetite regulation and metabolism.
3. What role does sleep play in hormone regulation?
Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of leptin and ghrelin, leading to increased hunger and cravings, contributing to weight gain.
4. Are there specific diets that can help balance hormones?
Diets rich in whole foods, healthy fats, and fiber can help regulate hormones like insulin and leptin, supporting healthy metabolism.
5. Can hormone replacement therapy help with weight loss?
In some cases, hormone replacement therapy can improve metabolic function and impact weight loss for those with hormonal deficiencies, such as hypothyroidism.
By recognizing the intricate relationships between hormones, weight, appetite, and metabolism, we can leverage this understanding to make impactful lifestyle changes. With this knowledge, we’re not just passive observers in the battle for health; we are empowered to take control. Dive into the power of hormones today—it could be the key to unlocking the best version of yourself.