Building Blocks of Well-Being: The Essential Relevance of Maslow’s Hierarchy Today
Introduction
In an ever-evolving world rife with challenges—from mental health crises to workplace burnout—understanding the fundamental aspects of well-being is more critical than ever. At the core of this exploration lies Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, a psychological framework that has stood the test of time. This article delves deep into the Building Blocks of Well-Being: The Relevance of Maslow’s Hierarchy Today, illustrating how this model not only applies to individual lives but also resonates in organizational culture, education, and community health.
The Power of Maslow’s Hierarchy
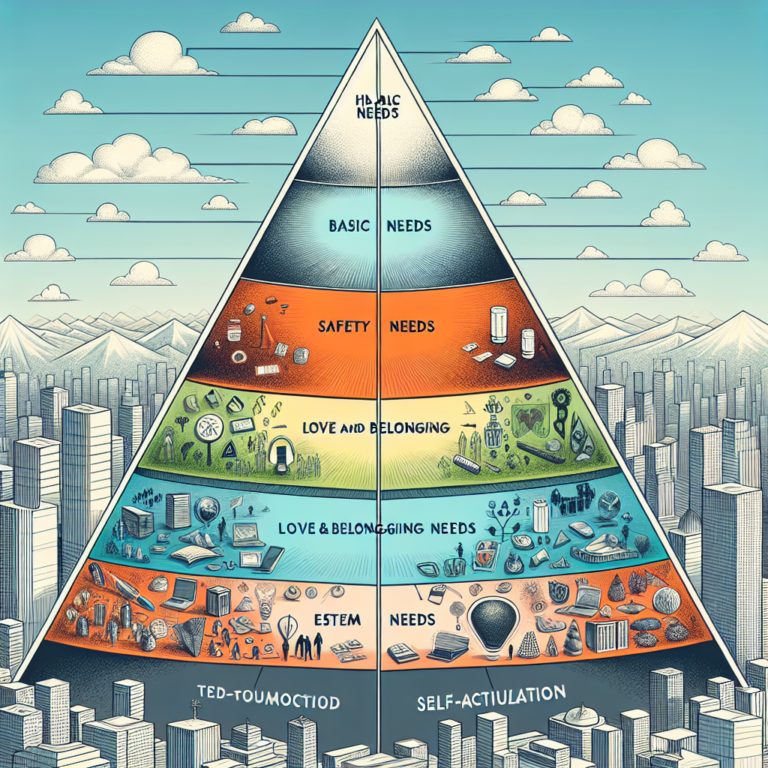
Abraham Maslow’s theory, introduced in 1943, posits that human motivation is based on a hierarchy of needs, often depicted as a pyramid. At its base are physiological requirements, ascending through safety, love and belonging, esteem, and finally culminating in self-actualization. Each level forms the foundational building blocks of well-being, creating a roadmap for individuals and organizations to understand motivational drivers.
The Five Levels of Maslow’s Hierarchy
1. Physiological Needs
The base of Maslow’s pyramid comprises our most basic needs: air, water, food, and shelter. Without these, our ability to focus on higher-level needs diminishes greatly.
Case Study: The Impact of Basic Needs in Crisis Situations
During the COVID-19 pandemic, it became evident how crucial physiological needs are. Many individuals faced food insecurity and lost their jobs, making it nearly impossible to think beyond immediate survival. Nonprofits that focused on food distribution highlighted the importance of meeting basic needs as a stepping stone toward addressing mental health and educational support.
2. Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, the next level is safety. This encompasses physical safety, financial security, health, and well-being.
Table: Safety Needs in Organizational Contexts
| Safety Needs | Examples in the Workplace |
|---|---|
| Physical Safety | Secure environments, safety drills |
| Financial Security | Benefits, job stability |
| Health | Insurance, wellness programs |
Organizations that prioritize employee safety report higher job satisfaction and productivity. Recognizing that these building blocks of well-being are interconnected can significantly improve workplace morale.
3. Love and Belonging
As humans, we are inherently social. This level emphasizes the importance of relationships—friendship, intimacy, and family.
Analysis: Community Building Exercises
Companies that invested in team building and social gatherings saw improved collaboration and creativity. For example, a tech firm that organized regular social events found that employees were more engaged and innovative, realizing that feeling connected was vital to their personal and organizational well-being.
4. Esteem Needs
Esteem encompasses the need for self-esteem, respect, status, and recognition. Achieving a sense of accomplishment is crucial for psychological health.
Case Study: Recognition Programs Boosting Employee Engagement
Let’s examine a retail company that launched a recognition program for its employees. They saw a 25% increase in employee engagement scores. This not only motivated the staff but also created an environment where individuals felt valued—essential ingredients in the building blocks of well-being.
5. Self-Actualization
At the pinnacle of Maslow’s pyramid, self-actualization is about realizing personal potential, self-fulfillment, and seeking personal growth and peak experiences.
Real-World Application: Lifelong Learning
Organizations that encourage continuous learning and self-improvement, such as providing training and development opportunities, often cultivate a culture of innovation and satisfaction.
The Relevance of Maslow’s Hierarchy Today
Impact on Mental Health
The increasing focus on mental health in today’s society emphasizes the importance of fulfilling Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Mental health initiatives in schools and workplaces are rooted in providing a secure foundation for individuals, underscoring the building blocks of well-being.
Organizational Culture
Organizations that adhere to Maslow’s framework tend to foster environments where employees feel secure and valued. Studies indicate that companies that emphasize well-being at work experience lower turnover and higher productivity, reinforcing the model’s relevance in today’s corporate culture.
Educational Settings
In education, understanding Maslow’s hierarchy allows educators to create environments conducive to learning. When students feel safe and connected, they are more likely to engage fully, demonstrating the application of building blocks of well-being in a classroom setting.
Societal Implications
On a broader scale, fulfilling these needs can lead to healthier societies. Policymakers can use Maslow’s hierarchy as a framework for addressing social issues, crafting policies that prioritize individuals’ basic needs before seeking higher-level goals.
The Future of Well-Being
As we move into a future that seemingly oscillates between progress and turmoil, the insights from Maslow’s theory will continue to serve as a guiding star. Whether it’s through individual self-management or organizational strategy, we must constantly revisit and evaluate how these building blocks of well-being are being addressed.
Conclusion
The relevance of Maslow’s hierarchy today cannot be overstated. From enhancing personal development to shaping organizational culture, the building blocks of well-being: the relevance of Maslow’s hierarchy today serve as a perpetual reminder of our foundational needs. As we navigate complexities in personal and professional lives, let us remember that fulfilling these needs is not merely a luxury but a necessity for true well-being.
Actionable Takeaway
As an actionable takeaway, consider conducting a personal or organizational audit using Maslow’s framework. Assess which needs may be unmet and explore strategies to address them. By doing so, you not only enhance your own well-being but could also positively influence those around you.
FAQs
1. How can Maslow’s hierarchy be applied in the workplace?
Maslow’s hierarchy can be implemented by ensuring employees’ basic needs are met, fostering a safe environment, promoting teamwork and camaraderie, recognizing achievements, and providing opportunities for personal growth.
2. Is Maslow’s hierarchy still relevant today?
Absolutely. While times have changed, the foundational needs described by Maslow continue to apply in various contexts, including mental health, workplaces, and education.
3. What are some examples of self-actualization in daily life?
Self-actualization can manifest through pursuing hobbies, continuing education, setting personal goals, or seeking out experiences that push personal boundaries.
4. How do the building blocks of well-being relate to mental health?
Meeting the needs within Maslow’s hierarchy can lead to improved mental health by alleviating stressors and providing a conducive environment for emotional stability.
5. What steps can organizations take to fulfill employees’ needs?
Organizations can conduct surveys to understand employees’ needs, implement safety protocols, organize team-building activities, offer recognition programs, and provide training for skill development.
In summary, Maslow’s hierarchy remains a powerful tool for understanding and enhancing well-being in the modern world. By addressing these foundational needs, we lay the groundwork for a healthier, happier society—one building block at a time.