In today’s ever-evolving workplace, the importance of inclusivity cannot be overstated. As organizations strive to create environments where every individual can thrive, assistive technologies have emerged as essential tools. This article delves into Assistive Technologies in the Workplace: Creating Inclusive Environments, exploring what they are, why they matter, and how they can significantly enhance workplace diversity and productivity.
Introduction
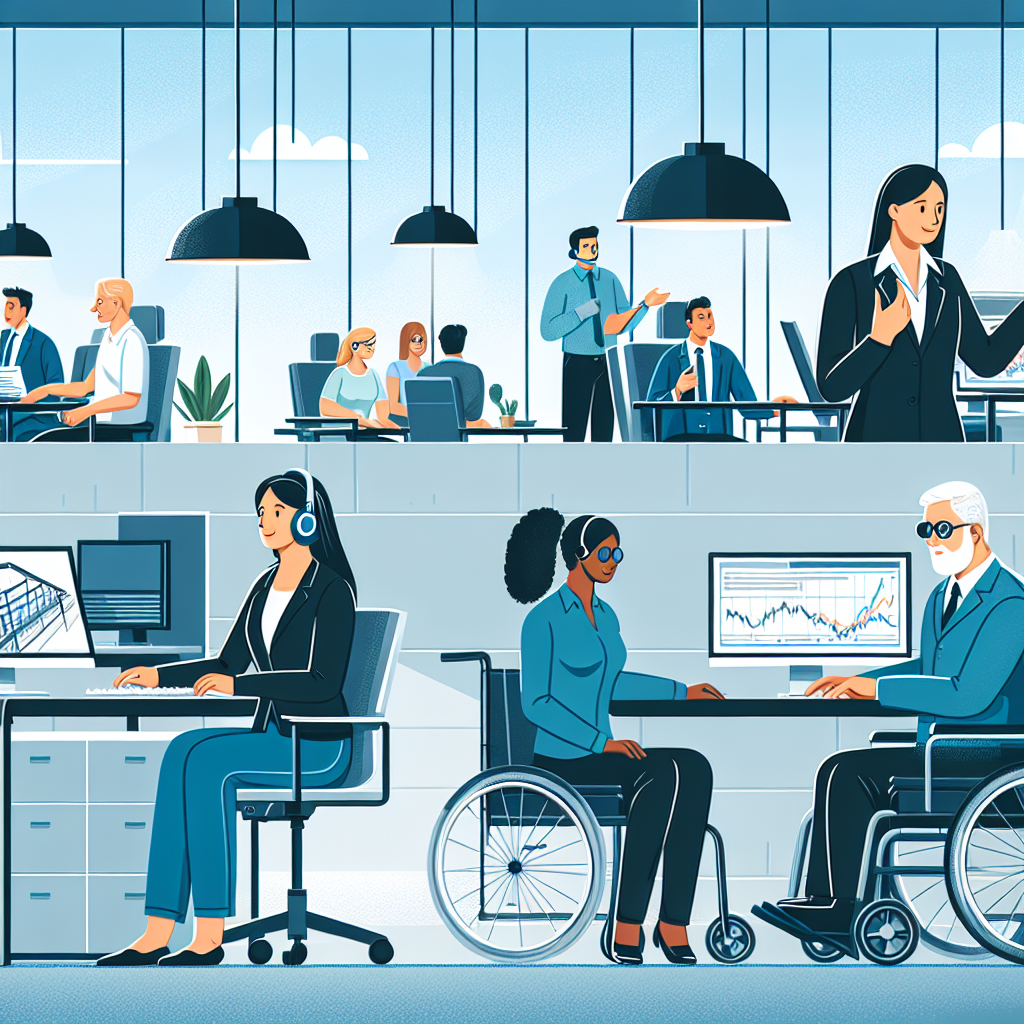
Imagine walking into a workplace where everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities, can contribute equally and effectively. This vision is increasingly being realized through assistive technologies. From screen readers for visually impaired employees to speech recognition software for those with limited mobility, assistive technologies are transforming how we perceive and enact inclusivity at work.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the profound impact of assistive technologies on creating inclusive workplaces. By highlighting real-world applications, success stories, and actionable insights, we aim to provide valuable information that can empower organizations to foster environments that embrace diversity.
What Are Assistive Technologies?
Assistive technologies are devices or software specifically designed to aid individuals with disabilities, helping them engage fully in various activities—including work. These technologies can range from simple tools, like ergonomic keyboards, to sophisticated software applications that facilitate communication or enhance cognitive function.
Categories of Assistive Technologies
- Mobility Aids: Tools that assist employees with physical impairments, such as wheelchairs, walkers, and modified workstations.
- Communication Aids: Devices like speech-generating devices (SGDs) and video relay service (VRS) that help employees communicate effectively.
- Cognitive Aids: Tools like reminder apps, scheduling software, and specialized workflows designed for individuals with cognitive disabilities.
- Sensory Aids: Technologies such as screen magnifiers and Braille displays tailored for employees with visual impairments.
Real-world Case Study: XYZ Corporation
At XYZ Corporation, assistive technologies transformed the workplace for one of their software developers who has a visual impairment. Implementing a screen reader and adaptability tools allowed this employee to contribute meaningfully to projects, leading to a notable increase in team productivity.
The Business Case for Inclusivity
Creating inclusive workplaces is not merely a compliance issue; it’s a strategic advantage. Organizations that prioritize Assistive Technologies in the Workplace: Creating Inclusive Environments stand to gain in numerous ways.
Benefits of an Inclusive Workplace
- Increased Productivity: Employees who feel included are more engaged and productive, contributing to greater overall success.
- Enhanced Innovation: Diverse teams foster creativity and innovation, which can lead to groundbreaking products and services.
- Improved Employee Retention: Organizations that prioritize inclusivity often experience lower turnover rates, saving costs related to hiring and training.
Data Supporting Inclusivity
| Metric | Inclusive Organizations | Non-Inclusive Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Employee Satisfaction (%) | 85 | 65 |
| Productivity Scores | 35% higher | – |
| Retention Rate (%) | 80 | 60 |
Implementing Assistive Technologies
Steps for Integration
- Assess Needs: Conduct surveys or interviews to understand the specific needs of employees with disabilities.
- Choose the Right Technologies: Research various assistive technologies and select those that align best with the identified needs.
- Training and Support: Provide thorough training for all employees to ensure seamless integration of assistive technologies.
- Continuous Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of implemented technologies and make adjustments as necessary.
Case Study: ABC Industries
ABC Industries implemented a variety of assistive technologies, including voice recognition software and screen readers. After a year of usage, employee feedback showed a 40% increase in satisfaction and a marked improvement in project turnover rates. The analysis highlighted that the inclusive technology investments led to a more collaborative atmosphere as team members were able to communicate more effectively.
Common Assistive Technologies in the Workplace
1. Screen Readers
For visually impaired employees, screen readers like JAWS or NVDA can be invaluable. These tools convert text on screens into speech, ensuring accessibility to information.
2. Speech Recognition Software
Programs like Dragon NaturallySpeaking allow users to control their computers and compose documents using voice commands, making it easier for employees with mobility challenges.
3. Adapted Keyboards and Mice
Ergonomic keyboards and specially designed mice can help those with limited dexterity work more comfortably and effectively.
4. Visual Alerts
Devices that provide visual alerts can assist employees who are hard of hearing, ensuring they receive critical information in real time.
Challenges to Implementation
Despite the clear benefits, organizations may face challenges when integrating assistive technologies. Common concerns include:
- Cost: Initial investment can be high, although it pays off through increased productivity.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may be hesitant to adopt new technologies. Proper education can mitigate this.
Overcoming Resistance
To overcome resistance, focus on:
- Clear communication regarding the benefits of assistive technologies.
- Involving employees in the selection and implementation process.
- Providing ongoing support and training.
Case Study: DEF Corp
DEF Corp faced initial resistance when introducing assistive technologies. By creating a training program that involved feedback and suggestions from employees with disabilities, they successfully eased the transition, resulting in a cohesive and engaged team.
Measuring the Impact of Assistive Technologies
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To determine the success of Assistive Technologies in the Workplace: Creating Inclusive Environments, organizations should track specific KPIs:
- Employee satisfaction scores
- Productivity levels pre- and post-implementation
- Retention rates over time
Real-world Example: GHI Solutions
At GHI Solutions, implementation of assistive technologies led to a 25% increase in productivity and a 30% improvement in employee satisfaction scores within one year. Regular surveys have become a part of their culture, allowing continuous iterative improvements.
Best Practices for Sustainability
1. Keep Abreast of New Technologies
Emerging assistive technologies offer new opportunities for enhancing inclusivity. Stay informed about developments in the field.
2. Maintain Open Lines of Communication
Encourage ongoing dialogue with employees to ensure their needs are met, adapting technology as required.
3. Foster a Culture of Inclusion
Promote an inclusive culture through workshops, events, and consistent messaging that values diversity and accessibility.
Conclusion
The journey towards creating inclusive workplaces through Assistive Technologies in the Workplace: Creating Inclusive Environments is both rewarding and essential. By advocating for and implementing these technologies, organizations not only comply with legal requirements but also foster creative and dynamic environments where all employees can thrive.
As we wrap up this discussion, remember that the goal of inclusivity is not merely compliance or corporate responsibility; it’s about recognizing the unique potential of every individual. Investing in assistive technologies is an investment in future productivity and innovation.
FAQs
1. What are the primary types of assistive technologies?
Assistive technologies include mobility aids, communication aids, cognitive aids, and sensory aids, among others.
2. How can I assess my workplace needs for assistive technologies?
Consider conducting surveys or focus groups to obtain input from employees with disabilities to gauge their specific needs.
3. Are assistive technologies expensive to implement?
While there can be initial costs, the long-term benefits in productivity and employee satisfaction often outweigh the expenses.
4. How can I ensure successful integration of assistive technologies?
Train employees thoroughly and create a culture of openness to help ease the transition.
5. What impact can assistive technologies have on a company’s culture?
Implementing these technologies fosters a more inclusive culture, promoting diversity and encouraging collaboration among all employees.
By focusing on Assistive Technologies in the Workplace: Creating Inclusive Environments, we can build not just functional workplaces but vibrant communities where everyone has the opportunity to succeed. Embrace this journey and witness the transformation that follows!